EU household energy consumption declines for second consecutive year
In 2023, energy consumption by households in the European Union dropped for the second year in a row, reaching 9.6 million terajoules. This represents a 5.6% decrease compared to 2022, when 10.1 million terajoules were recorded. The decline follows the sector’s highest-ever level of consumption in 2021, which peaked at 11.0 million terajoules.
Households accounted for 26.2% of the EU’s final energy consumption last year. The primary energy sources used in this sector were natural gas (29.5%), electricity (25.9%), and renewables and biofuels (23.5%).
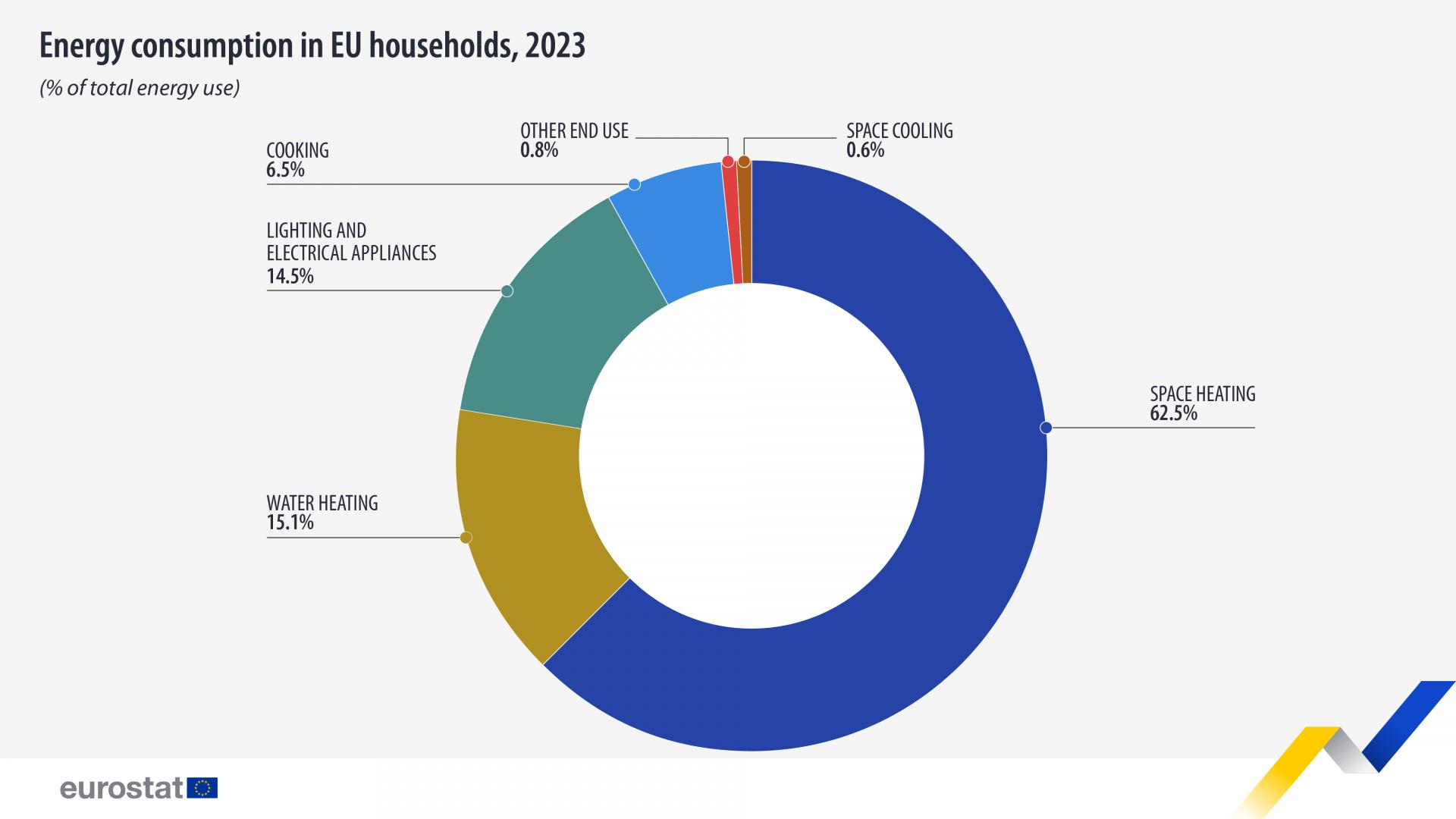
The largest share of household energy consumption was used for space heating, which made up 62.5% of the total. Water heating accounted for an additional 15.1%, meaning that together, heating functions represented 77.6% of residential energy use.
Lighting and electrical appliances—excluding heating, cooling, and cooking—comprised 14.5% of the total, while cooking accounted for 6.5%. Space cooling and other uses remained minimal, with shares of 0.6% and 0.8% respectively.
The continued decline in household energy use reflects broader trends in energy efficiency and conservation across the EU.